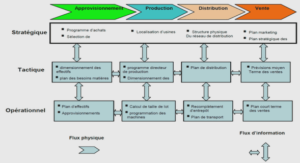
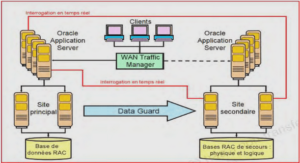
RAC Architecture
Disk architecture
With today’s SAN and NAS disk storage systems, sharing storage is fairly easy and is required for a RAC environment, you can use the below storage setups SAN (Storage Area Networks) – generally using fibre to connect to the SANNAS ( Network Attached Storage) – generally using a network to connect to the NAS using either NFS, ISCSI JBOD – direct attached storage, the old traditional way and still used by many companies as a cheap option All of the above solutions can offer multi-pathing to reduce SPOFs within the RAC environment, there is no reason not to configure multi- pathing as the cost is cheap when adding additional paths to the disk because most of the expense is paid when out when configuring the first path, so an additional controller card and network/fibre cables is all that is need. The last thing to think about is how to setup the underlining disk structure this is known as a raid level, there are about 12 different raid levels that I know off, here are the most common ones
There are many other raid levels that can be used with a particular hardware environment for example EMC storage uses the RAID-S, HP storage uses Auto RAID, so check with the manufacture for the best solution that will provide you with the best performance and resilience. Raw Volumes – normally used for performance benefits, however they are hard to manage and backupCluster FileSystem – used to hold all the Oracle datafiles can be used by windows and linux, its not used widelyAutomatic Storage Management (ASM) – Oracle choice of storage management, its a portable, dedicated and optimized cluster filesystem I will only be discussing ASM, which i have already have a topic on called Automatic Storage Management.Oracle ClusterwareOracle Clusterware software is designed to run Oracle in a cluster mode, it can support you to 64 nodes, it can even be used with a vendorThe Clusterware software allows nodes to communicate with each other and forms the cluster that makes the nodes work as a single logical server. The software is run by the Cluster Ready Services (CRS) using the Oracle Cluster Registry (OCR) that records and maintains the cluster and node membership information and the voting disk which acts as a tiebreaker during communication failures. Consistent heartbeat information travels across the interconnect to the voting disk when the cluster is running.
The OPROCd daemon provides the I/O fencing for the Oracle cluster, it uses the hangcheck timer or watchdog timer for the cluster integrity. It is locked into memory and runs as a realtime processes, failure of this daemon results in the node being rebooted. Fencing is used to protect the data, if a node were to have problems fencing presumes the worst and protects the data thus restarts the node in question, its better to be save than sorry. The CRSd process manages resources such as starting and stopping the services and failover of the application resources, it also spawns separate processes to manage application resources. CRS manages the OCR and stores the current know state of the cluster, it requires a public, private and VIP interface in order to run. OCSSd provides synchronization services among nodes, it provides access to the node membership and enables basic cluster services, including cluster group services and locking, failure of this daemon causes the node to be rebooted to avoid split-brain situations.
The last component is the Event Management Logger, which runs the EVMd process. The daemon spawns a processes called evmlogger and generates the events when things happen. The evmlogger spawns new children processes on demand and scans the callout directory to invoke callouts. Death of the EVMd daemon will not halt the instance and will be restarted.The cluster-ready services (CRS) is a new component in 10g RAC, its is installed in a separate home directory called ORACLE_CRS_HOME. It is a mandatory component but can be used with a third party cluster (Veritas, Sun Cluster), by default it manages the node membership functionality along with managing regular RAC-related resources and services